Respiration (physiology)
호흡(呼吸)은 체내에 산소를 받아들이고 이산화탄소를 배출하는 생명 활동이다.[1]
개요
생물은 소화와 흡수로 얻은 영양 물질을 산화시켜 생명 활동에 필요한 에너지를 얻는다. 산화에는 산소가 필수 요소이므로 생물은 호흡을 통해 산소를 체내 또는 세포로 받아들인다.[2]
효모와 같은 일부 미생물은 산소가 없는 상태에서도 주위의 당분과 같은 물질을 이용하여 호흡할 수 있는데 이를 무산소 호흡이라 한다.[3]
세포 단위에서 이루어 지는 호흡을 내호흡이라 하며 미토콘드리아에서 산소를 받아들여 영양분을 산화시켜 에너지를 얻는다. 이 때 발생한 에너지는 ATP에 저장되어 사용된다.[4]
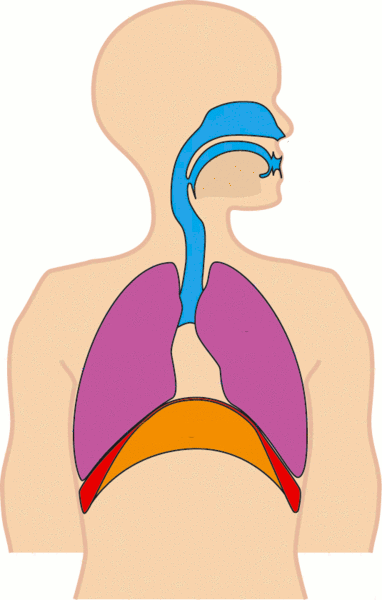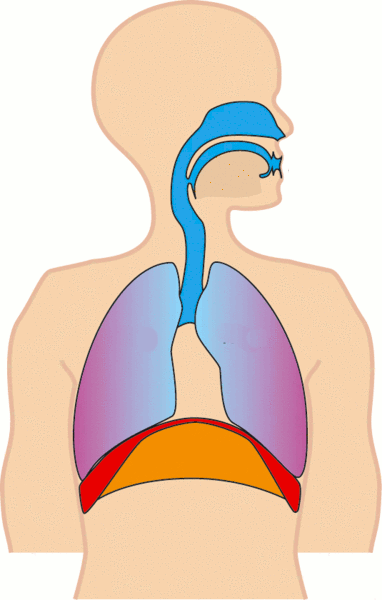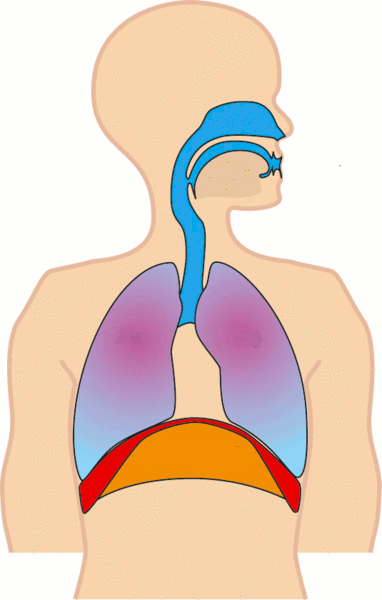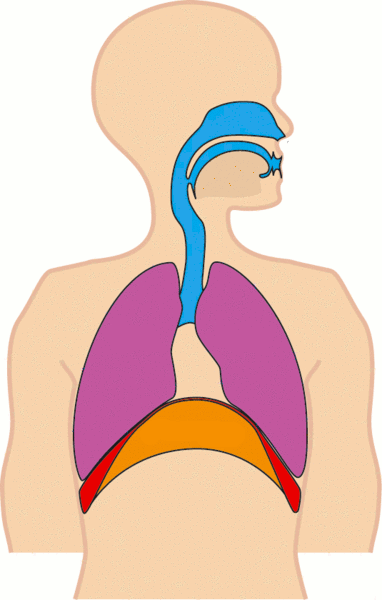
고등생물은 몸 안으로 산소를 받아들이고 이산화탄소를 배출하는 역할을 전담하는 호흡 기관이 있다.
수생 동물의 경우 아가미가 이에 해당하며 육상 생물은 허파가 이에 해당한다.
외호흡
- 이 부분의 본문은 호흡 기관입니다.
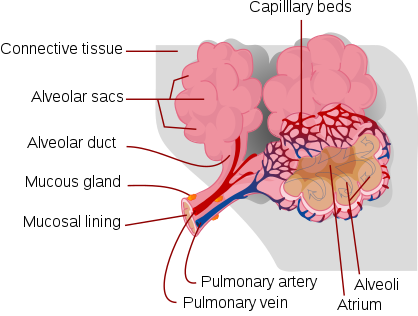
허파나 아가미와 같은 호흡 기관에서 이루어 지는 기체 교환을 외호흡이라 한다.
외호흡은 호흡운동을 통해 공기나 수중의 산소를 체내로 받아들이고 이산화탄소를 몸 밖으로 배출하는 생명활동이다.
인간의 경우 횡경막과 내-외 늑간근의 운동으로 허파에 공기를 받아들이고 이산화탄소를 배출한다. 보통 1분에 15 - 18회의 호흡이 이루어 지며 한 번에 받아들이는 공기는 약 500ml이다. 건강한 성인 남자의 경우 최대 폐활량은 약 4,800 ml에 이른다.[2]
내호흡
세포 안에서 일어나는 내호흡은 포도당의 해당 과정 등에서 나온 에너지를 ATP에 저장하는 과정이다.
내호흡의 과정은 해당 과정, TCS 회로, 전자 전달계의 세 과정으로 나누어 살필 수 있다.[4]
- 해당 과정: 해당 과정은 한개의 포도당 분자를 두개의 피브루산으로 분리하는 일련의 생화학과정으로 10 종류의 효소가 이 과정에 관여한다. 이 화학 반응에서 포도당의 분해 결과 발생한 에너지는 2개의 ATP에 저장된다. 포도당의 해당 과정은 아래의 화학식으로 표현될 수 있다.
- TCA 회로: 해당 과정에서 만들어진 피브루산은 세포 내의 미토콘드리아로 옯겨 진다. 미토콘드리아에서 피브루산은 탈수소효소와 탈탄산효소에 의해 이산화탄소와 수소 원자로 분해되며 이 과정에서 하나의 ATP가 생성된다. 또한 이 때 발생하는 이산화탄소는 혈액에 의해 운반되어 호흡기관을 통해 몸 밖으로 배출 된다. TCA 회로에서 일어나는 화학 반응은 아래와 같다.
- 전자전달계: 해당과정과 TCA 회로에 의해 분리된 수소 원자는 미토콘드리아 내막으로 운반되어 수소 이온이 되며, 전자전달계라 불리는 일련의 과정을 통해 산소와 결합하여 물을 만들고 이 과정에서 발생한 에너지가 ATP 합성효소에 전달되어 ATP가 생성된다.[5]
내호흡을 통해 만들어진 ATP는 갖가지 생명 활동에 에너지를 공급한다.
'건강하고 행복하게 > 建康 運動' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Exercise physiology (0) | 2009.04.01 |
|---|---|
| 근력운동과 호흡 (0) | 2009.02.16 |
| Ischaemic heart disease (0) | 2009.02.08 |
| Myocardial Ischemia, Injury and Infarction (0) | 2009.02.08 |
| ★ 고혈압과 운동 Hypertension and exercise ★ (0) | 2009.02.06 |