Nasal Cavity 鼻腔
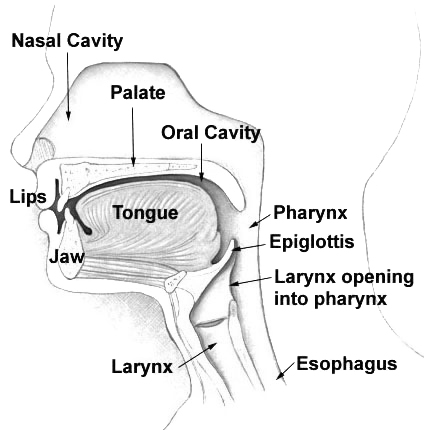
The nasal cavity (or nasal fossa) is a large air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face.
The nasal cavity conditions the air to be received by the areas of the respiratory tract and nose. Owing to the large surface area provided by the conchae, the air passing through the nasal cavity is warmed or cooled to within 1 degree of body temperature. In addition, the air is humidified, and dust and other particulate matter is removed by vibrissae, short, thick hairs, present in the vestibule. The cilia of the respiratory epithelium move the particulate matter towards the pharynx where it is swallowed.
Paranasal Sinus 副鼻腔
Types in humans
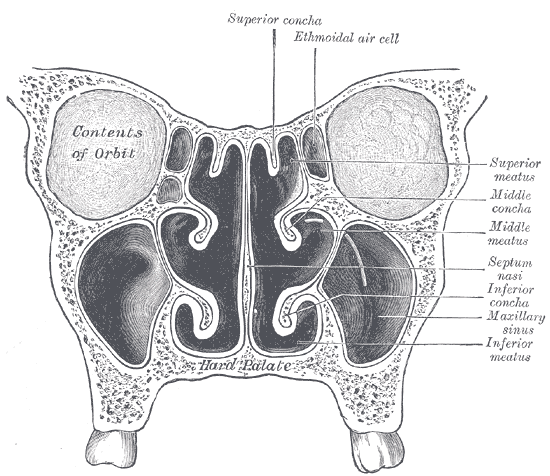
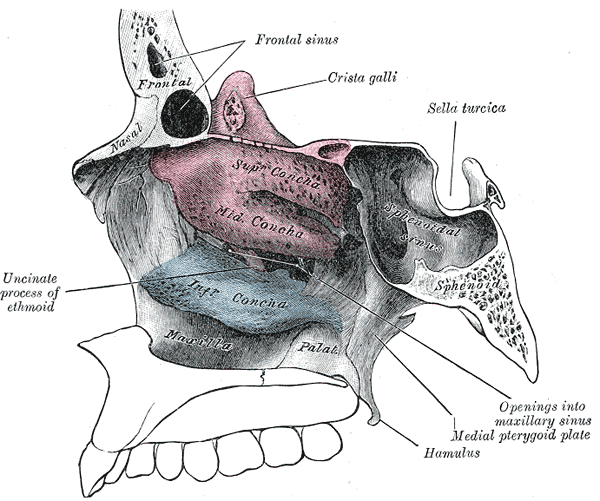
Humans possess a number of paranasal sinuses, divided into subgroups that are named according to the bones within which the sinuses lie:
- the maxillary sinuses, also called the maxillary antra and the largest of the paranasal sinuses, are under the eyes, in the maxillary bones (cheek bones).
- the frontal sinuses, over the eyes, in the frontal bone, which forms the hard part of the forehead.
- the ethmoid sinuses, which are formed from several discrete air cells within the ethmoid bone between the nose and the eyes.
- the sphenoid sinuses, in the sphenoid bone at the center of the skull base under the pituitary gland.
'연구하는 인생 > Anatomy' 카테고리의 다른 글
| THE BRAIN (0) | 2012.03.03 |
|---|---|
| http://www.ithaca.edu/faculty/lahr/LE2000/LE_index.html (0) | 2011.06.05 |
| Human brain (0) | 2011.01.18 |
| BRAIN 腦 (0) | 2011.01.18 |
| Thrombus 血栓 (0) | 2011.01.18 |