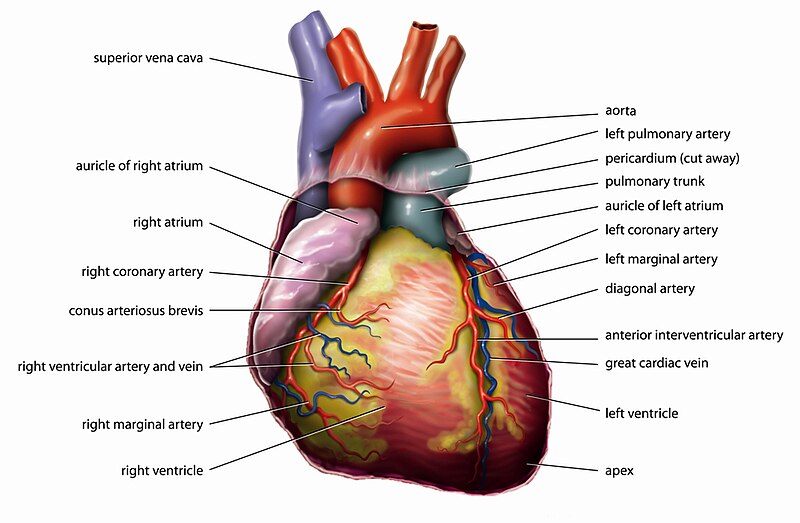
The human heart is a muscular organ that provides a continuous blood circulation through the cardiac cycle and is one of the most vital organs in the human body.[1] It is divided into four main chambers: the two upper chambers are called the left and right atria and two lower chambers are called the right and left ventricles.There is a thick wall of muscle separating the right side and the left side of the heart called the septum. Normally the right ventricle pumps the same blood amount into the lungs with each bit that the left ventricle pumps out. Physicians commonly refer to the right atrium and right ventricle together as the right heart and to the left atrium and ventricle as the left heart.[2]
The electric energy that stimulates the heart occurs in the sinoatrial node, which produces a definite potential and then discharges, sending an impulse across the atria. The Purkinje fibers transmit the electric charge to the myocardium while the cells of the atrial walls transmit it from cell to cell, making the atrial syncytium. The heart is an organ but made up of a collection of tissues.
The human heart and its disorders (cardiopathies) are studied primarily by cardiology.
Structure
The human heart has a mass of between 250 and 350 grams and is about the size of a fist.[3]
It is enclosed in a double-walled protective sac called the pericardium.[4] The superficial part of this sac is called the fibrous pericardium. This sac protects the heart, anchors its surrounding structures, and prevents overfilling of the heart with blood.
The outer wall of the human heart is composed of three layers. The outer layer is called the epicardium, or visceral pericardium since it is also the inner wall of the pericardium. The middle layer is called the myocardium and is composed of muscle which contracts. The inner layer is called the endocardium and is in contact with the blood that the heart pumps. Also, it merges with the inner lining (endothelium) of blood vessels and covers heart valves.[5]
The human heart has four chambers, two superior atria and two inferior ventricles. The atria are the receiving chambers and the ventricles are the discharging chambers.
The pathways of blood through the human heart are part of the pulmonary and systemic circuits. These pathways include the tricuspid valve, the mitral valve, the aortic valve, and the pulmonary valve.[6] The mitral and tricuspid valves are classified as the atrioventricular (AV) valves. This is because they are found between the atria and ventricles. The aortic and pulmonary semi-lunar valves separate the left and right ventricle from the pulmonary artery and the aorta respectively. These valves are attached to the chordae tendinae (literally the heartstrings), which anchors the valves to the papilla muscles of the heart.
The interatrioventricular septum separates the left atrium and ventricle from the right atrium and ventricle, dividing the heart into two functionally separate and anatomically distinct units.
[edit] Functioning
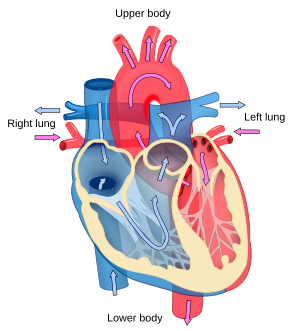
Blood flows through the heart in one direction, from the atria to the ventricles, and out of the great arteries, or the aorta for example. Blood is prevented from flowing backwards by the tricuspid,bicuspid, aortic, and pulmonary valve.
The heart acts as a double pump.
The function of the right side of the heart (see right heart) is to collect de-oxygenated blood, in the right atrium, from the body (via superior and inferior vena cavae) and pump it, via the right ventricle, into the lungs (pulmonary circulation) so that carbon dioxide can be dropped off and oxygen picked up (gas exchange). This happens through the passive process of diffusion.
The left side (see left heart) collects oxygenated blood from the lungs into the left atrium.
From the left atrium the blood moves to the left ventricle which pumps it out to the body (via the aorta).
On both sides, the lower ventricles are thicker and stronger than the upper atria.
The muscle wall surrounding the left ventricle is thicker than the wall surrounding the right ventricle due to the higher force needed to pump the blood through the systemic circulation.
Starting in the right atrium, the blood flows through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. Here, it is pumped out of the pulmonary semilunar valve and travels through the pulmonary artery to the lungs. From there, blood flows back through the pulmonary vein to the left atrium. It then travels through the mitral valve to the left ventricle, from where it is pumped through the aortic semilunar valve to the aorta and to the rest of the body. The (relatively) deoxygenated blood finally returns to the heart through the inferior vena cava and superior vena cava, and enters the right atrium where the process began.
Lifestyle and heart health
Obesity, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol can increase the risk of developing heart disease. However, half the number of heart attacks occur in people with normal cholesterol levels. Heart disease is a major cause of death (and the number one cause of death in the Western World.[citation needed]
It is generally accepted that factors such as exercise, diet, and overall well-being, including both emotional and physiological components, affect heart health in humans.[7][8][9][10]
heart
'연구하는 인생 > Anatomy' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Thrombus 血栓 (0) | 2011.01.18 |
|---|---|
| Trigger Point / trigger site (0) | 2011.01.05 |
| The Muscles and Fasciæ of the Hand (0) | 2009.11.09 |
| Pressure point 急所 (0) | 2009.09.17 |
| TRIGGER POINT (0) | 2009.09.17 |